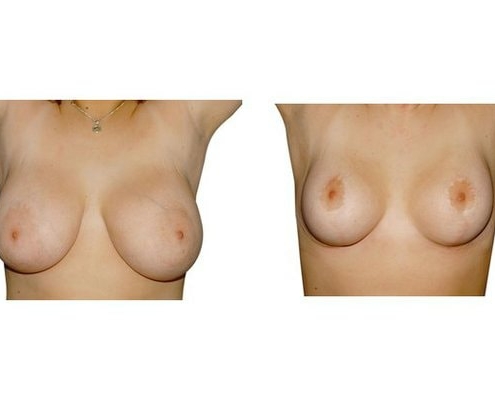
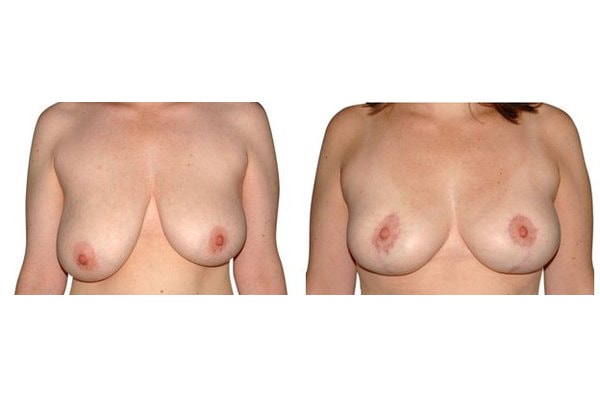
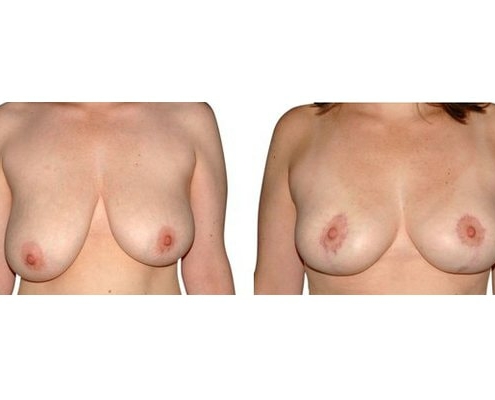
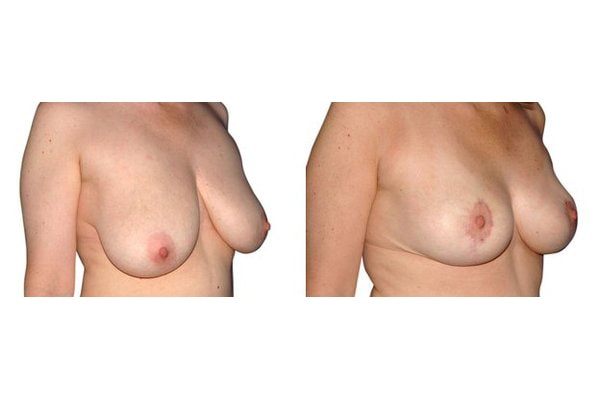
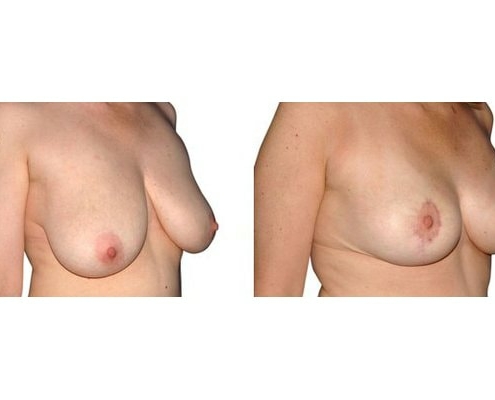
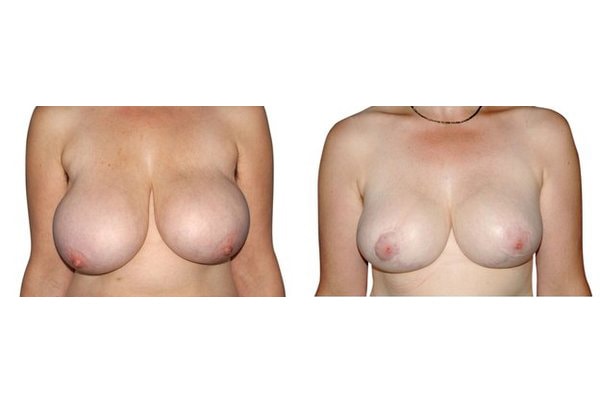
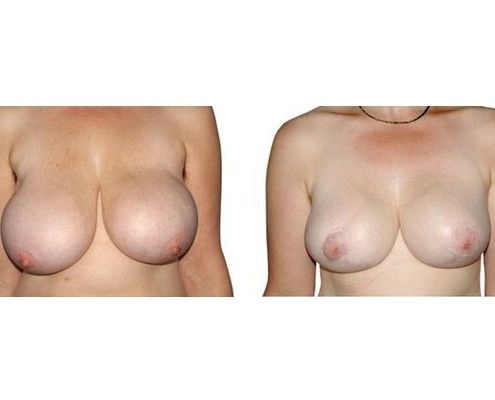
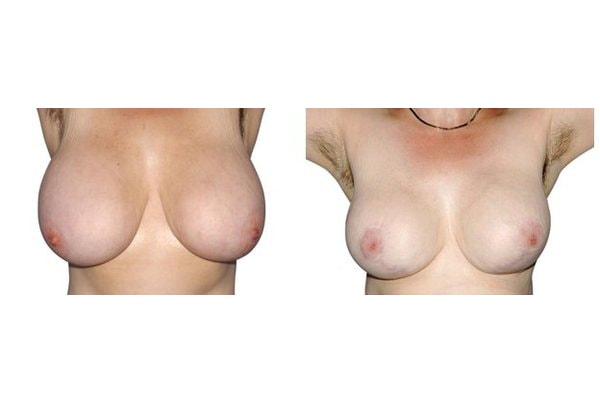
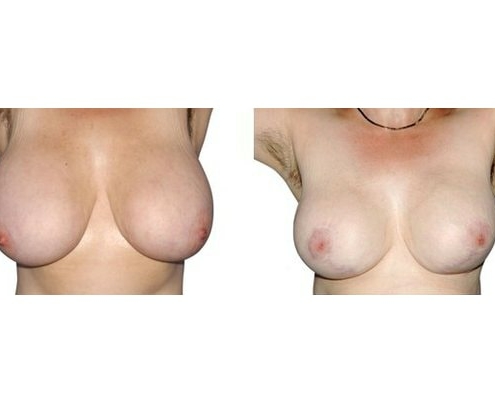
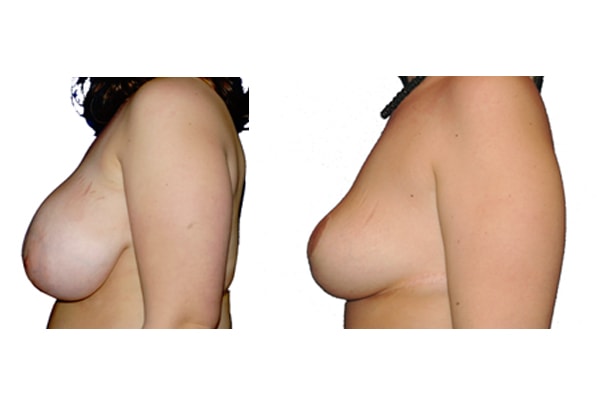
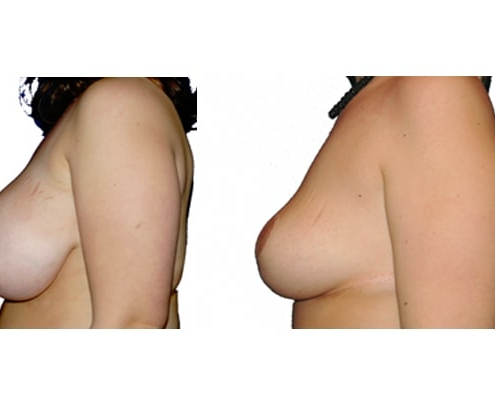
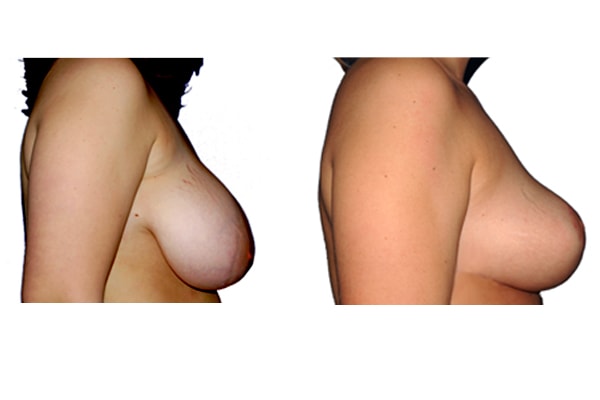
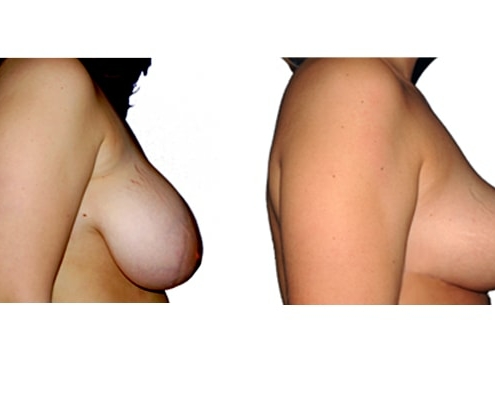
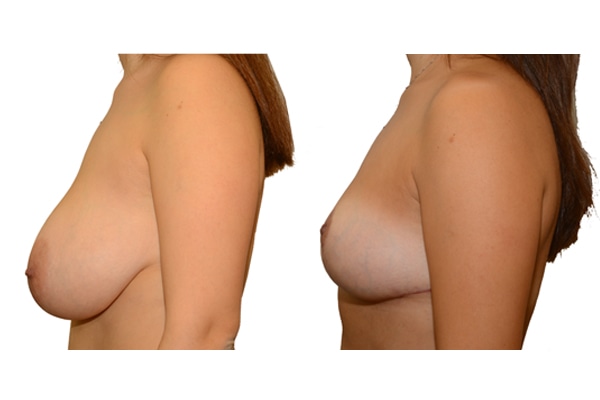
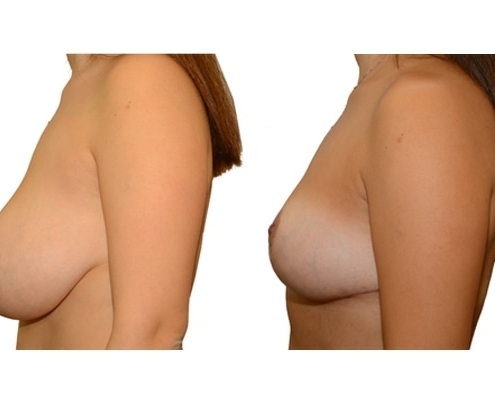
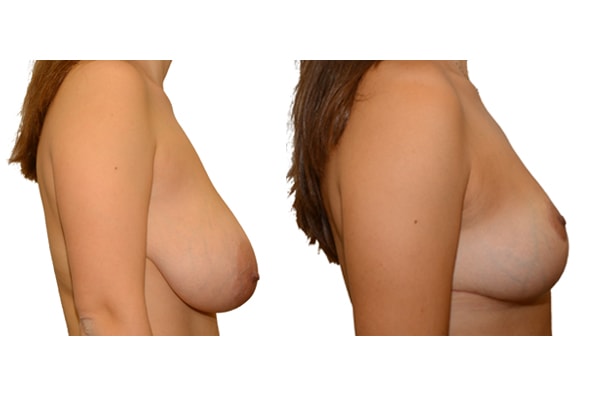
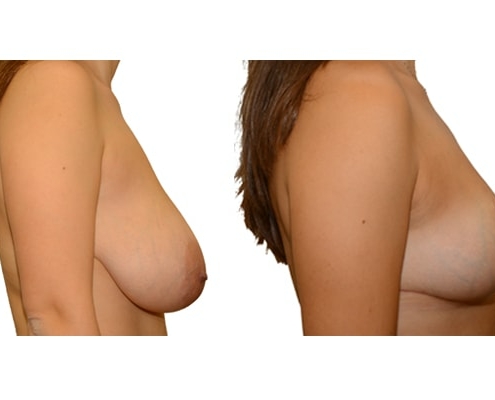
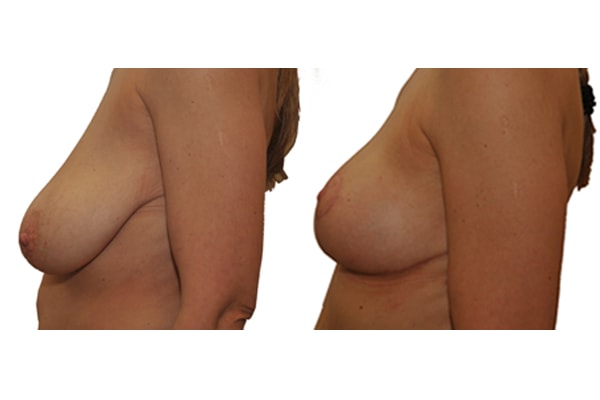
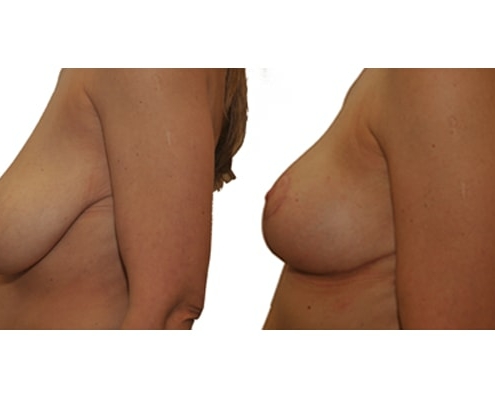
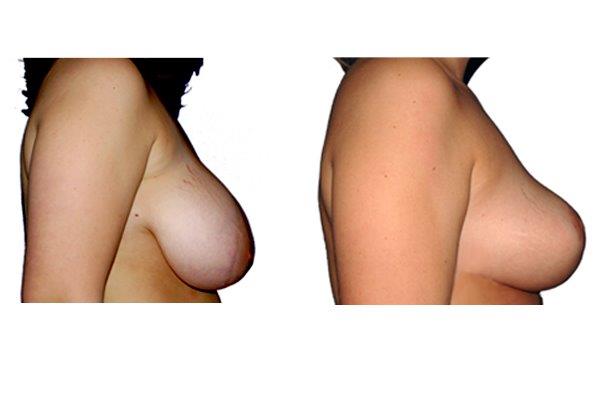
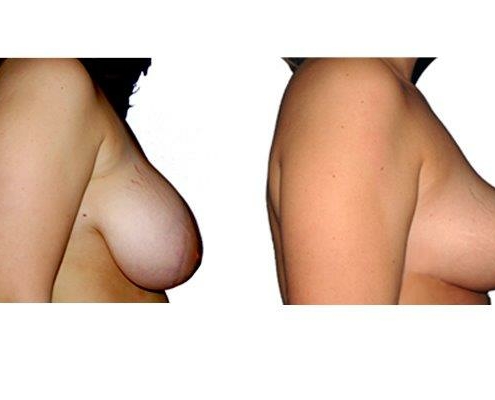
1. At what age and until what age can a breast reduction be performed?
A breast reduction should not be carried out prior to 18 years of age. Growth in size and breast growth should be completed. If the family planning is not yet complete, a method should be used which takes into account the sensitivity of the nipples and the ability to breastfeed. There is no upper limit if you are medically and psychologically sound.
2. What methods of breast reduction surgery are available?
There are well over 100 different surgical procedures, which differ radically in the incision and in the type of tissue removal. Please discuss with your surgeon the pros and cons of the methods used.
3. How do the various methods of breast reduction differ?
They differ in the course of scarring, method of tissue removal, characteristic of blodd supply of nipple and areola, the preservation of the sensitivity/excitability of the nipples, the shaping of the breast and not least in the durability of the surgical result. Depending on which of these aspects are particularly important for the patient, different techniques are selected.
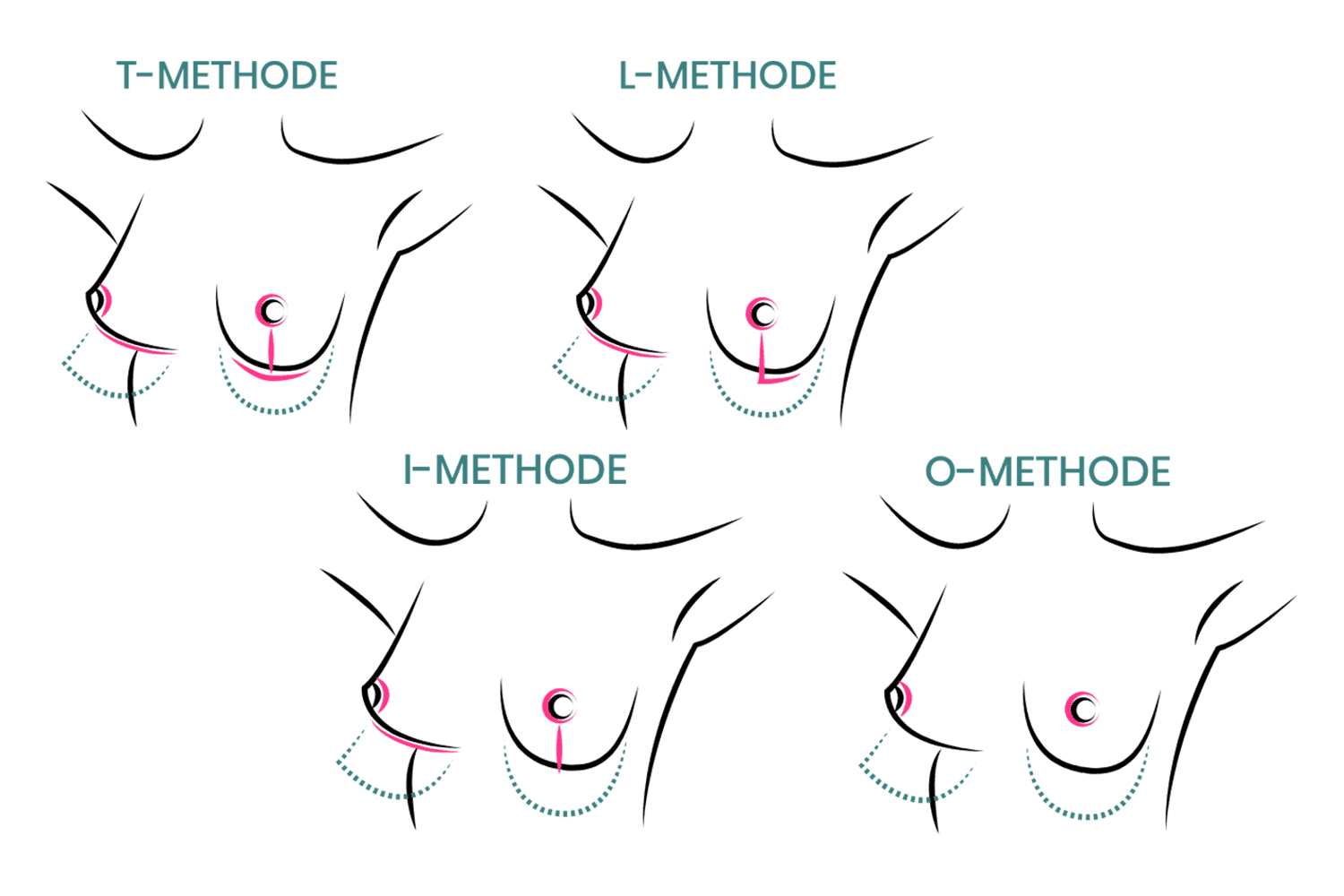
4. What possible types of scarring are there?
Scarring can progress like an inverted T (Anchor), looking down and out from the areola, run vertically down or be confined to the areola. The anchor-shaped incision is the most effective proceudre and permits best shaping of the breast. Scar-saving techniques can be used, if not much tissue must be removed or if the necessary lift of the areola is not very long (<10 cm).
5. During a breast reduction, can a large areola also be reduced?
A reduction of the areola is in the context of a breast reduction possible and is routinely carried out if necessary at no extra cost.
6. Can a breast reduction be carried out under local anesthesia?
A breast reduction is a comprehensive intervention, which should be carried out under general anesthesia.
7. Will I lose the ability to breastfeed with a breast reduction?
Generally not, however, in rare cases, the ability to breastfeed may be affected. Only when using non-contemporary methods (free mammary transplant) is the ability to breastfeed completely lost.
8. Will I lose the sensitivity of the nipples with a breast reduction?
There are ways that jeopardize the sensitivity of the nipples less than others, but have several disadvantages. If sensitivity is particularly important, you should tell your doctor.
9. What complications can occur?
The most common medical complication is bleeding, followed by infection and impaired wound healing (necrosis of the skin and/or the areola). When performed correctly, they are very rare. Other complications can include asymmetry in size and shape, distorted areolas and widened scars. Aesthetic complications can almost always be corrected. For serious medical complications (necrosis, etc.), this is unfortunately not always possible.
10. How long after the procedure can I expect to be fit again?
In general, normal activity can be resumed after 10-14 days.
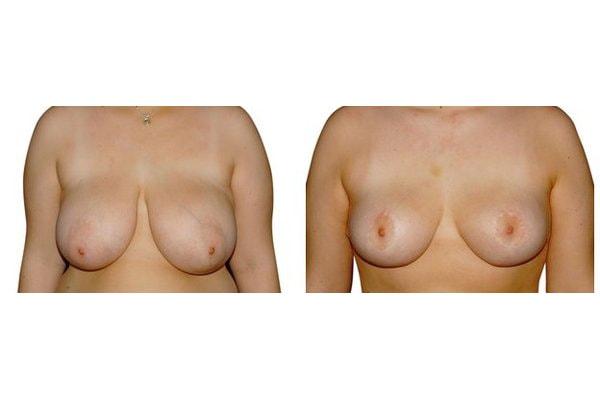
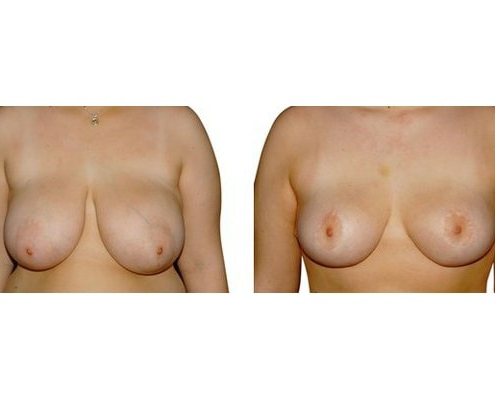
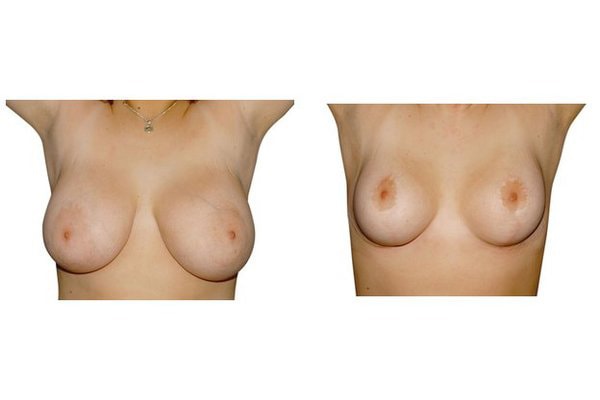
11. What are the long-term results after breast reduction?
In the vast majority of breast reductions, long-term results are generally very good. Keep weight fluctuations and pregnancies limited to increase the possibility. A reduced breast usually keeps its size. The situation is somewhat different with the durability of the result. How long the result lasts and as from the time it starts to drop and/or bottoms out again, depends on the weight of the breast (gravitiy) and the individual properties of the tissue (loose or tight connective tissue) and the method used.