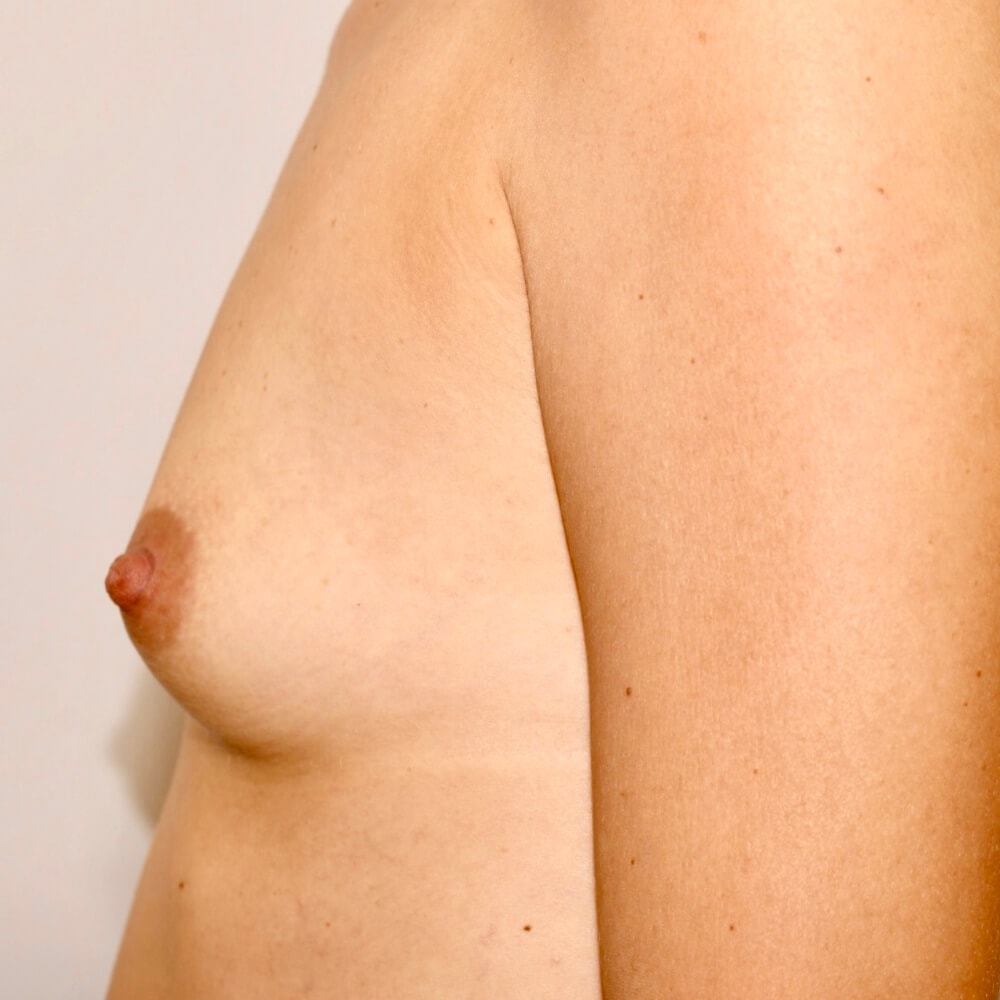
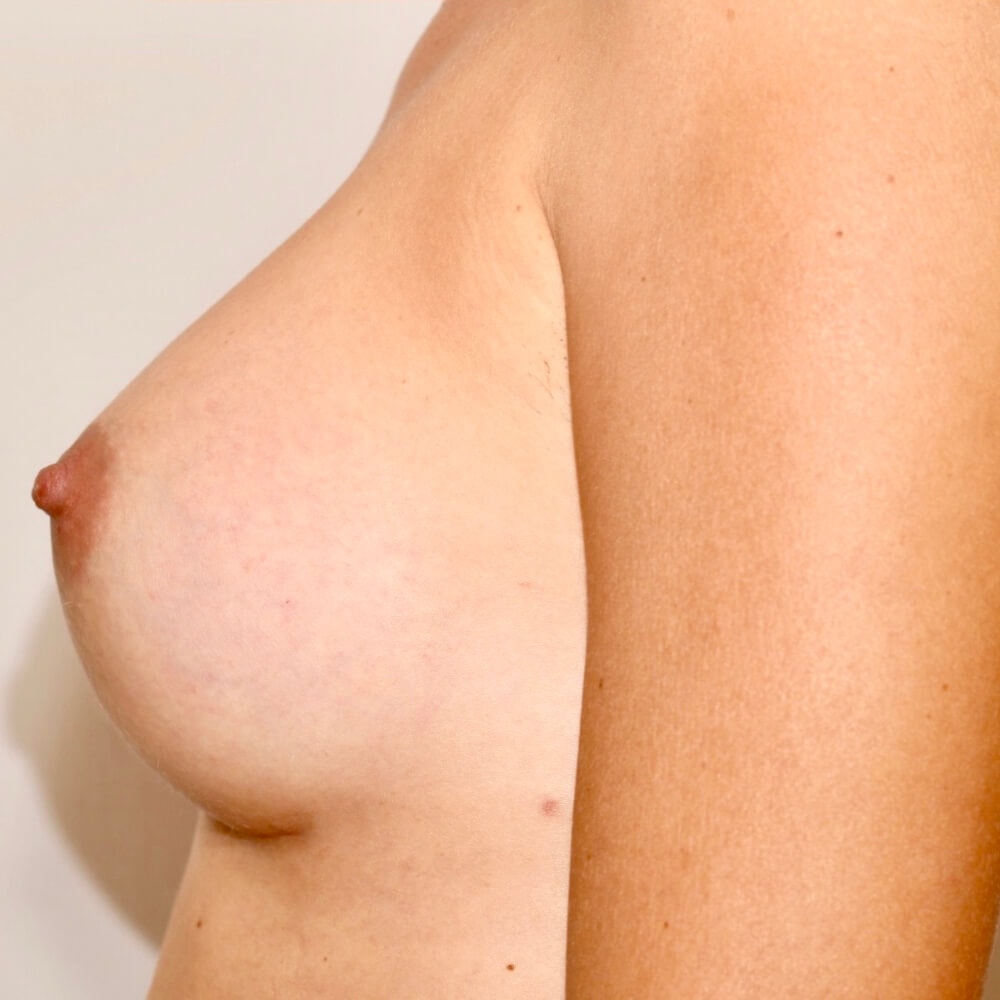
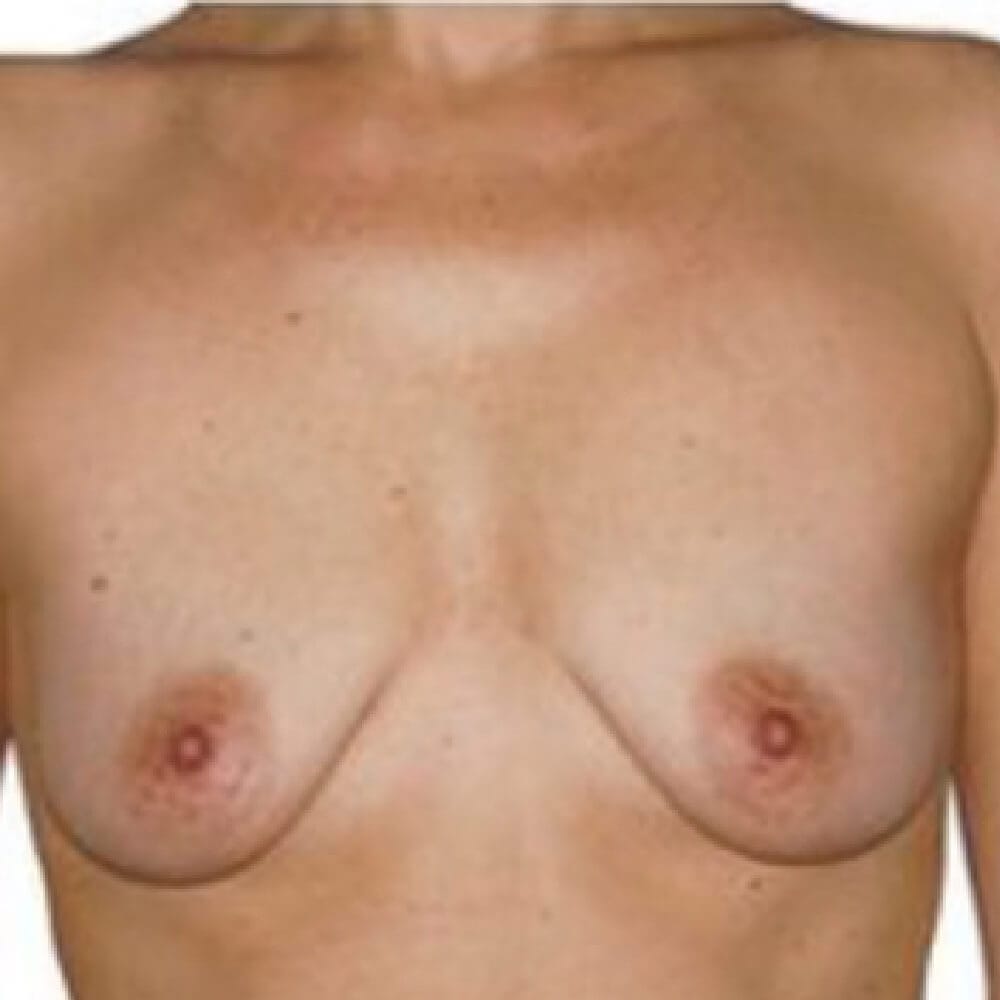
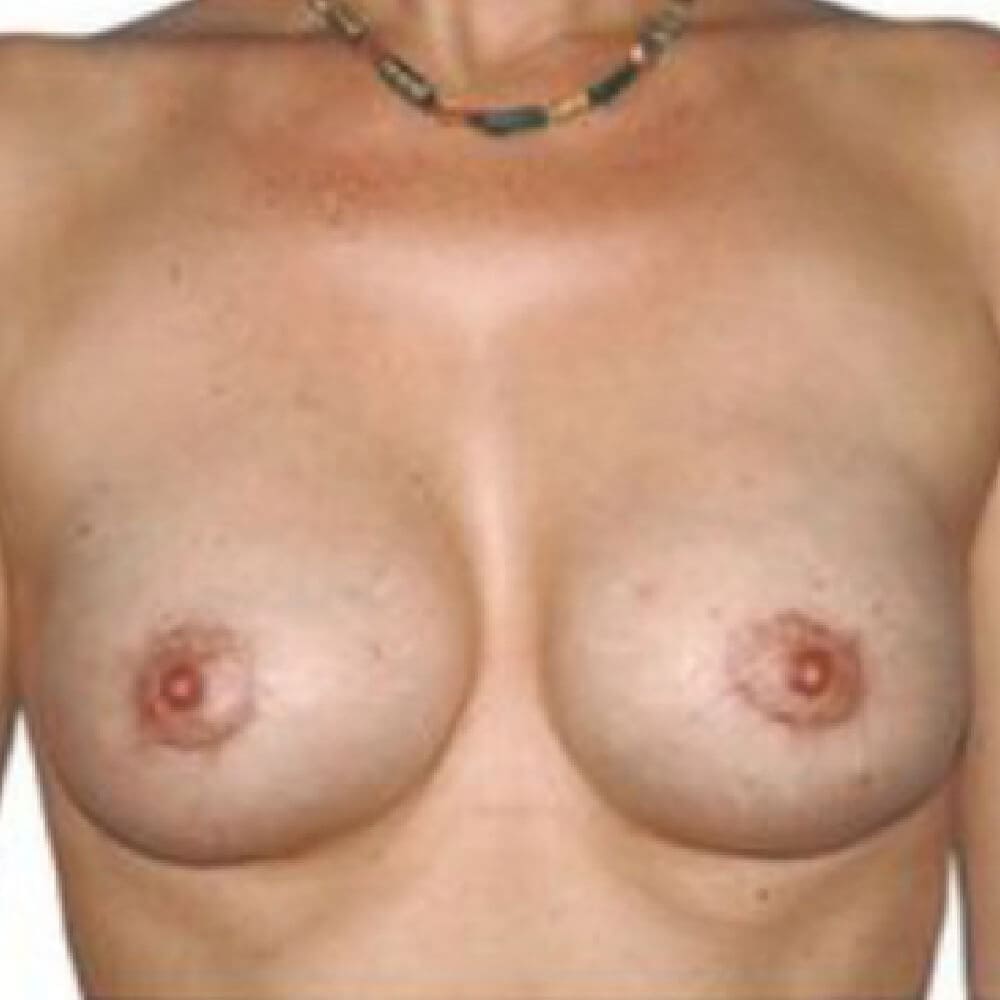
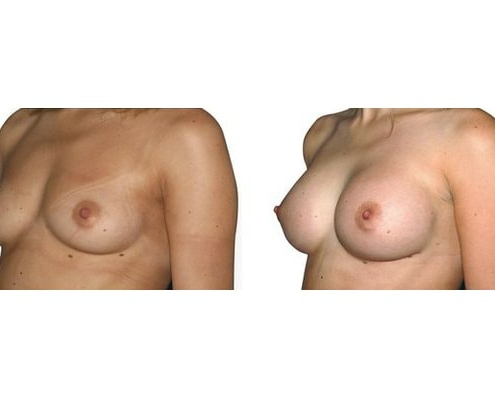
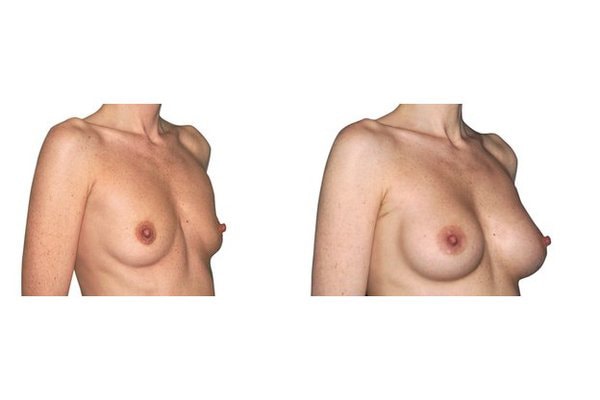
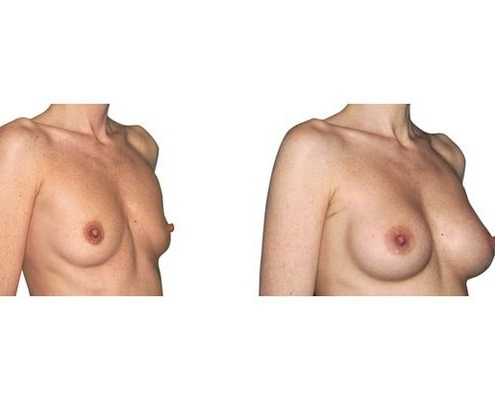
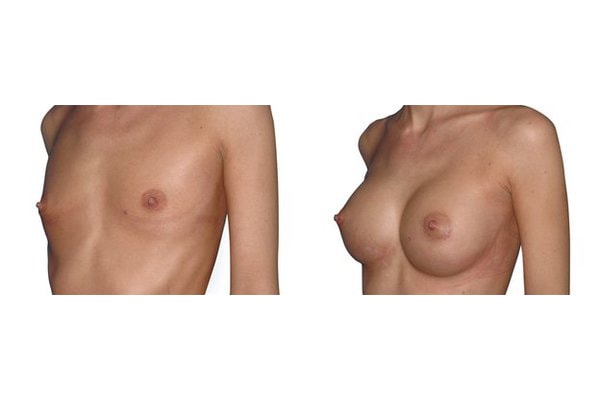
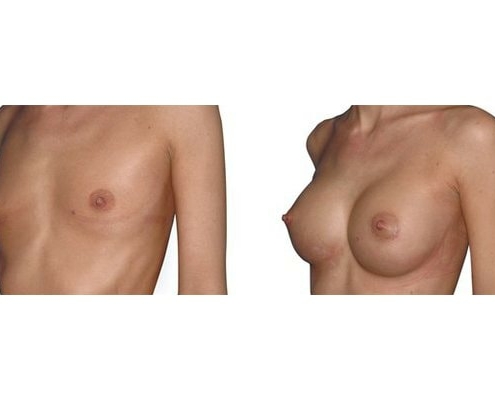
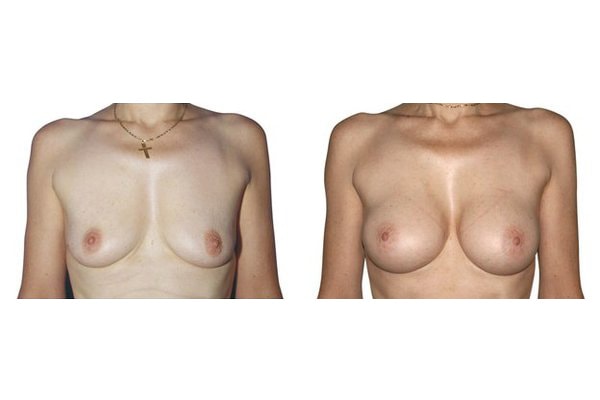
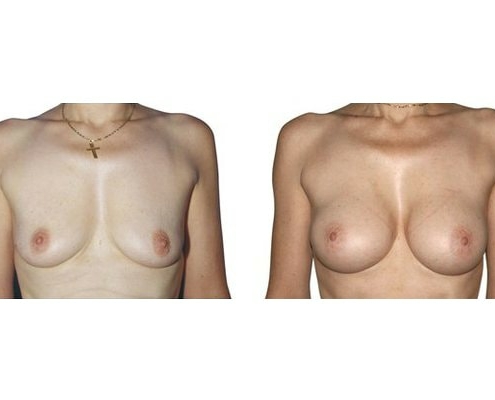
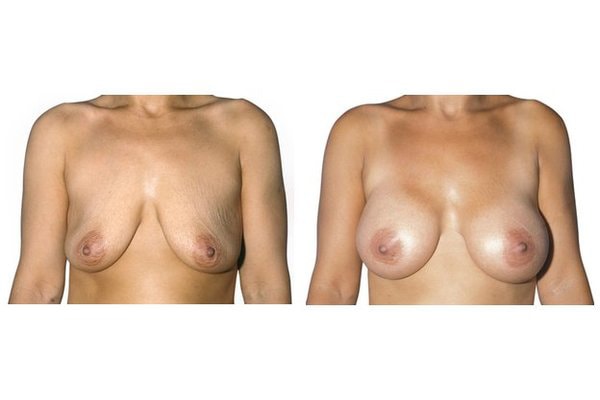
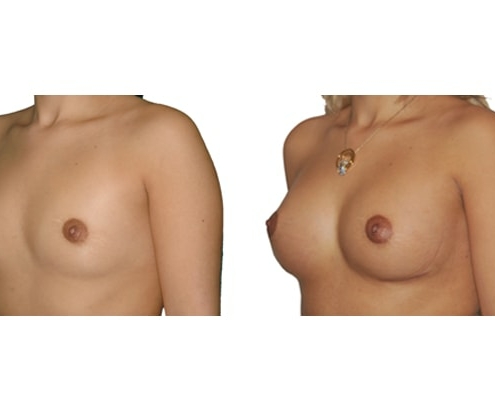
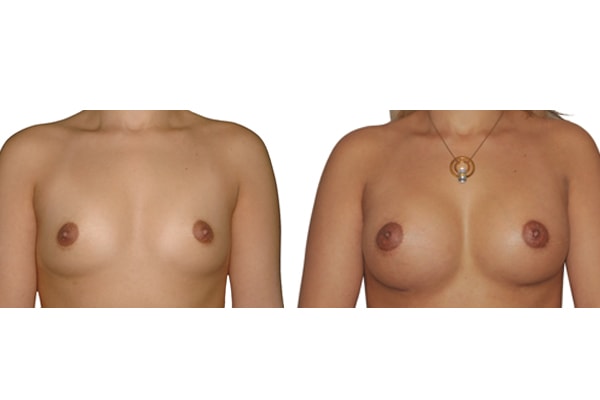
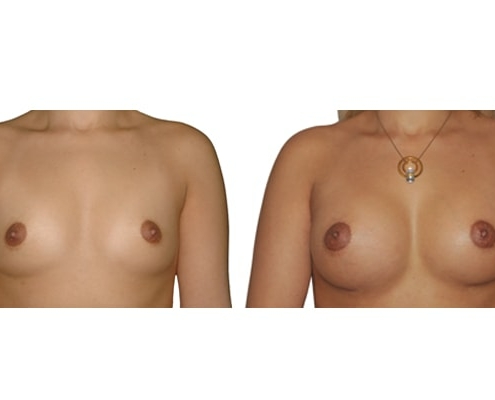
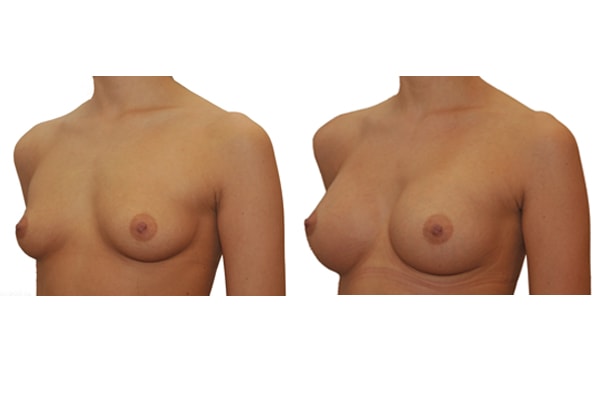
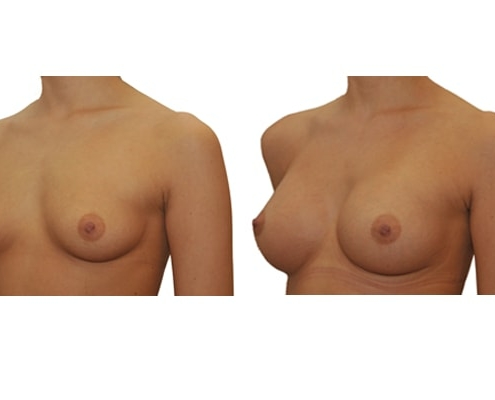
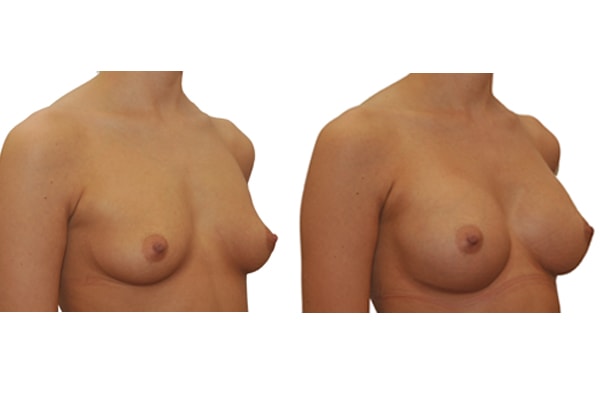
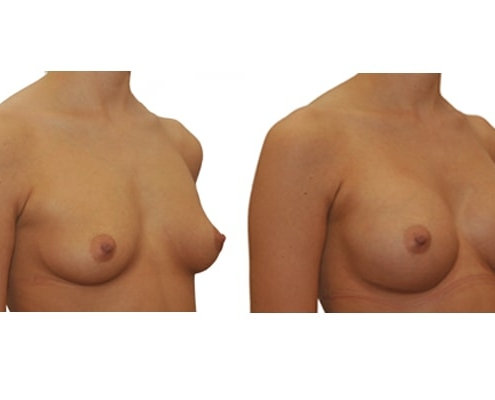
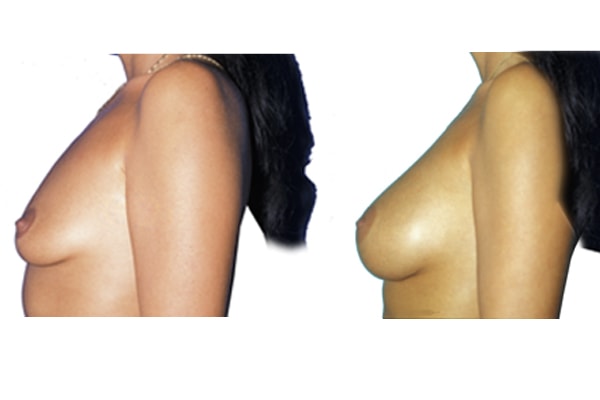
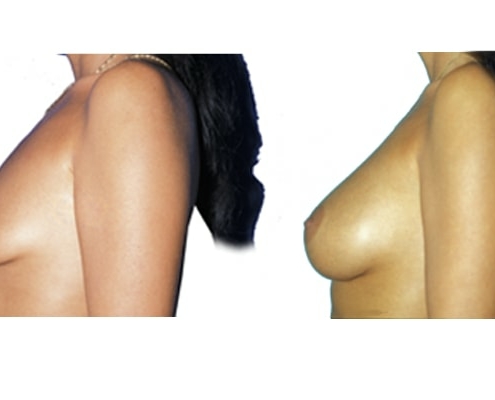
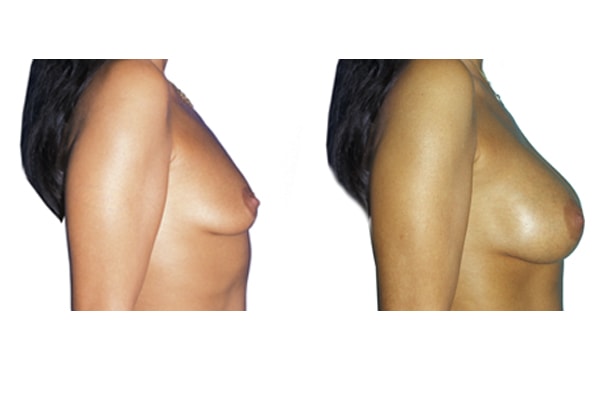
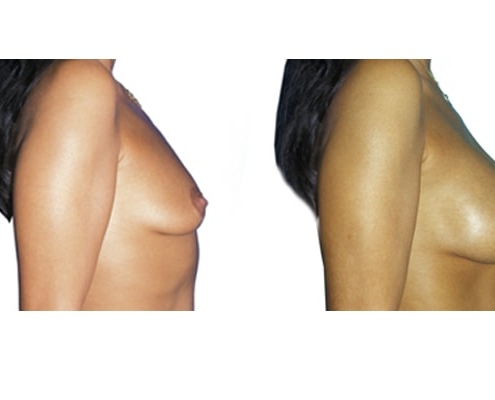
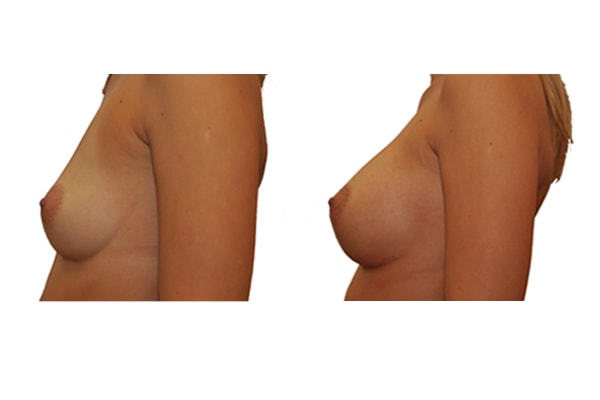
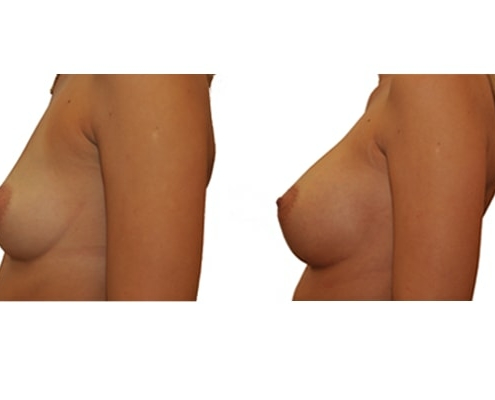
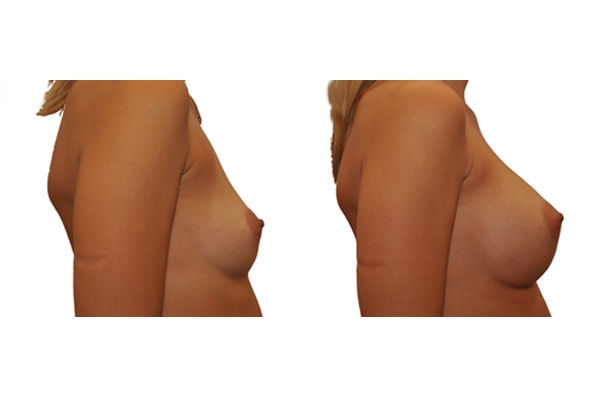
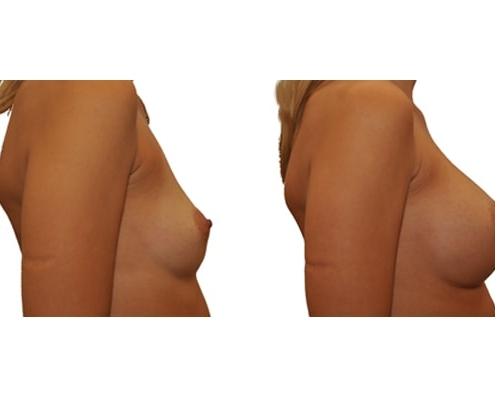
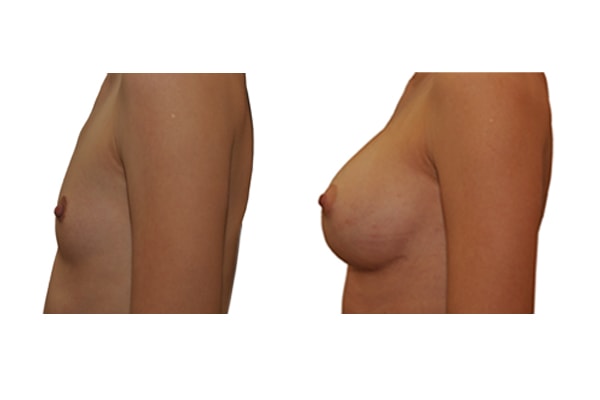
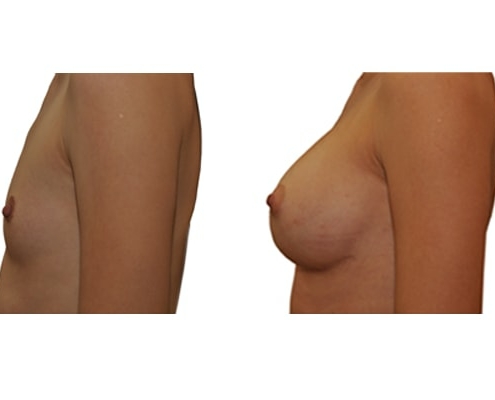
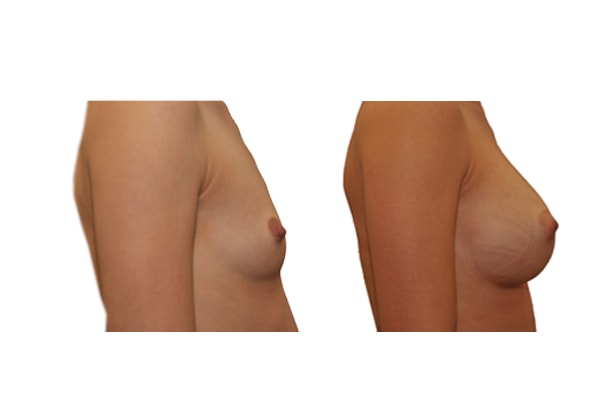
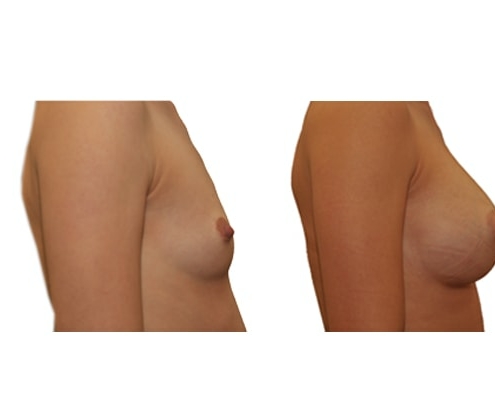
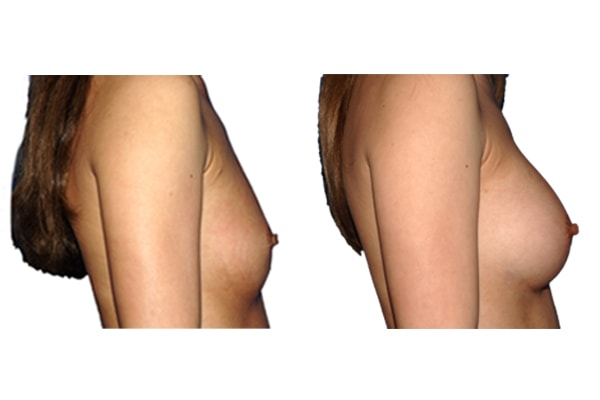
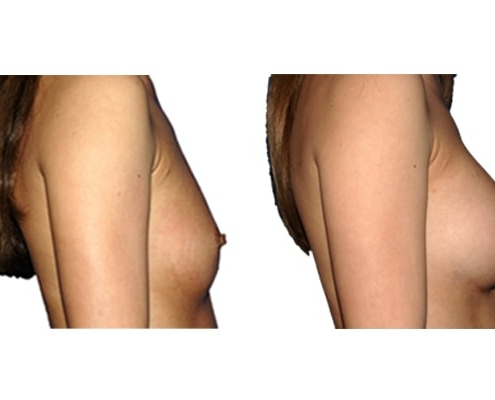
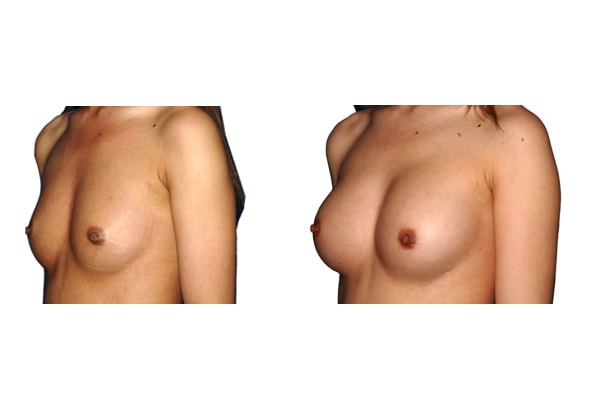
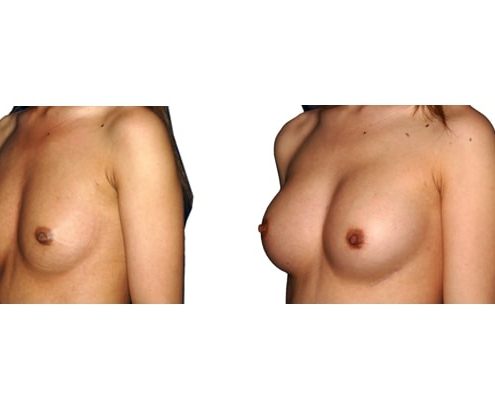
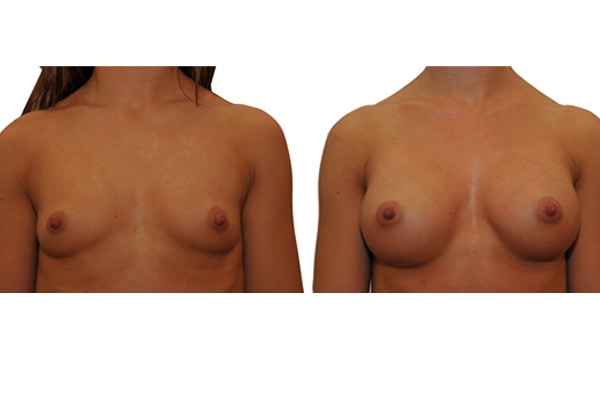
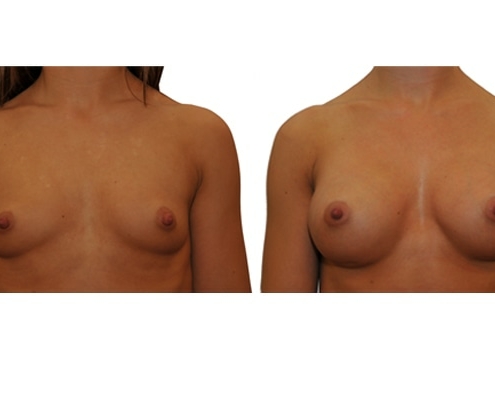
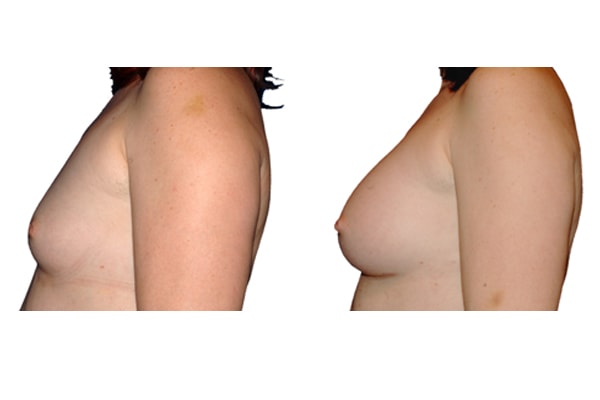
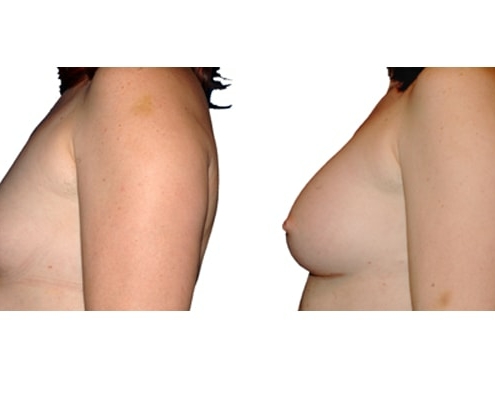
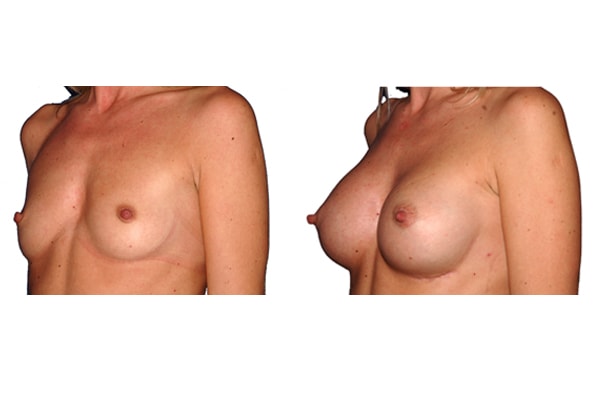
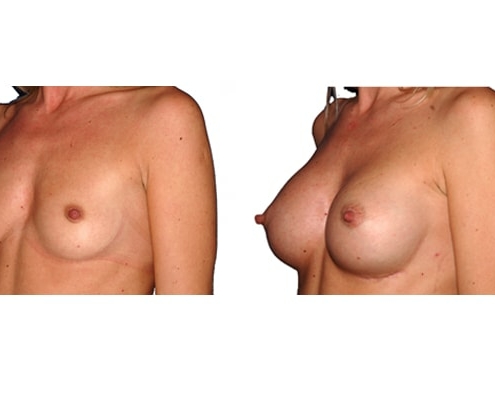
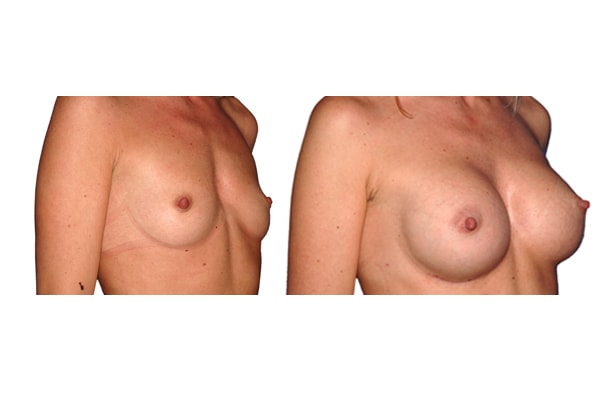
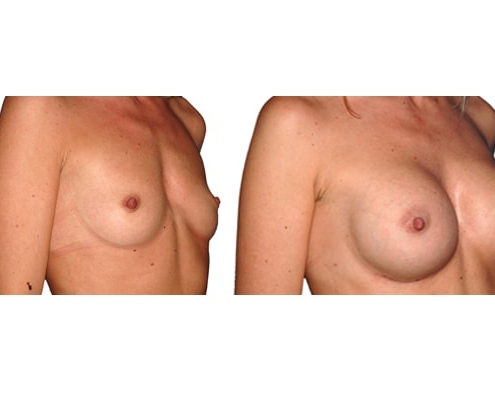
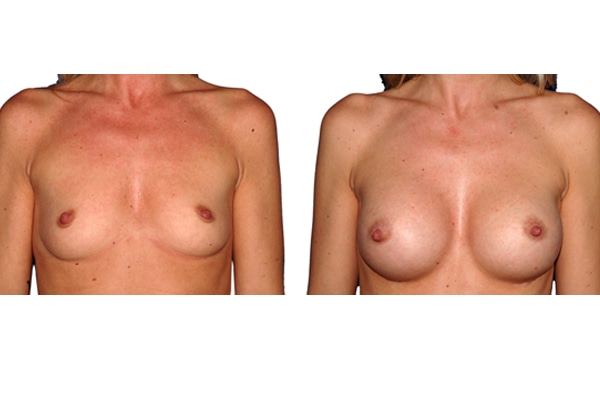
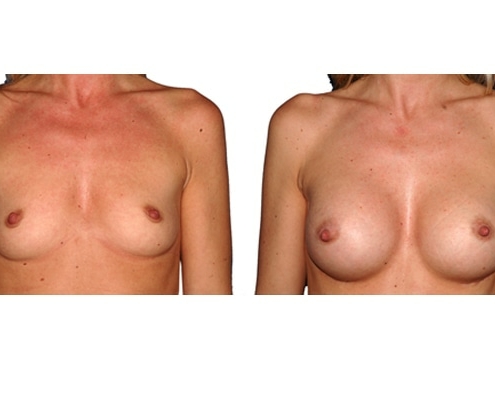
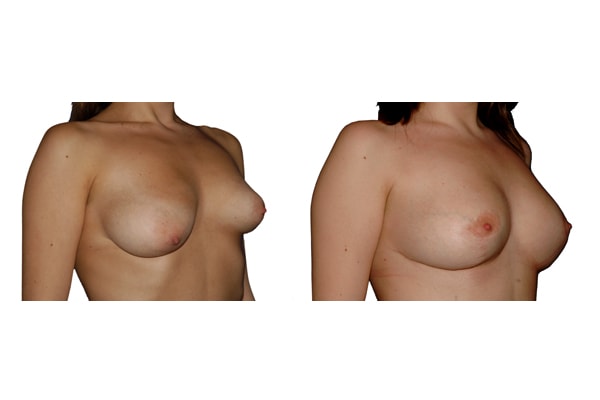
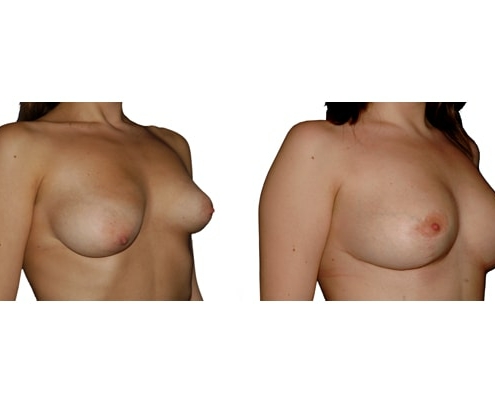
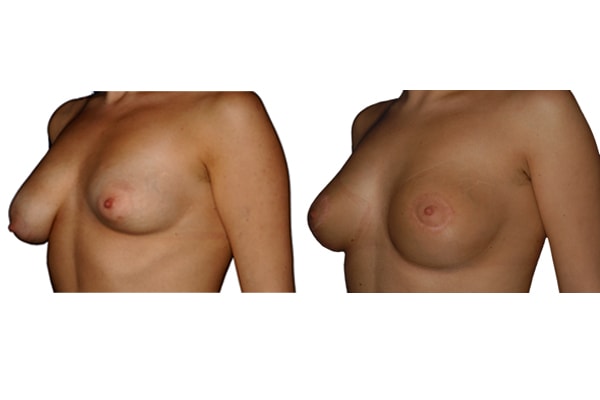
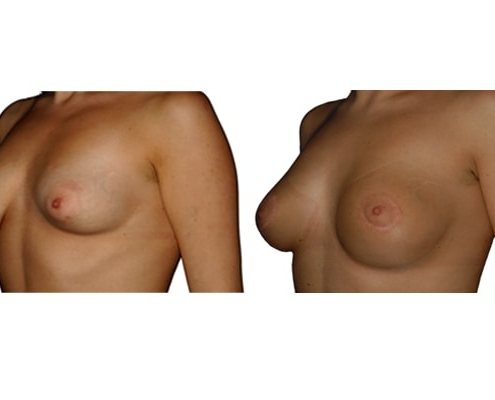
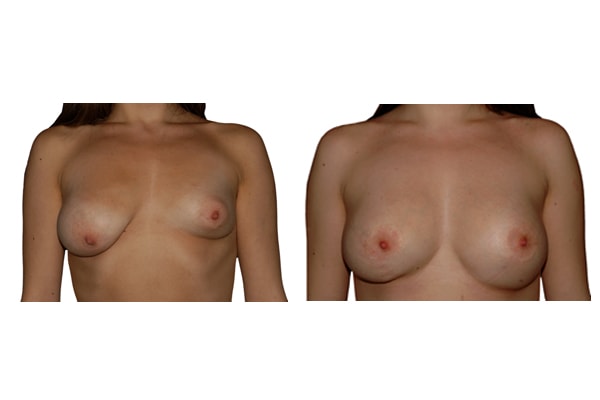
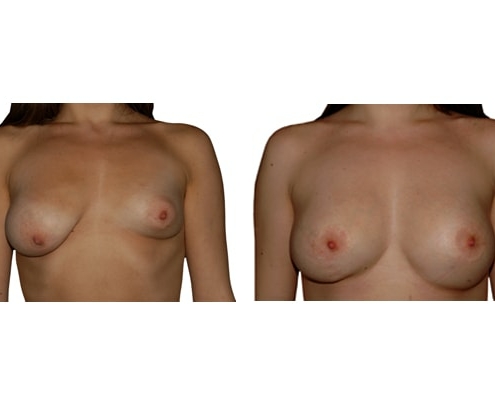
1. Do silicone gel implants cause breast cancer?
No, this issue is now finally resolved. At the 11th World Congress of Plastic Surgery in Yokohama in 1995 several studies, conducted worldwide, were presented, which had investigated the link between breast implants and breast cancer. In no study could correlations be established and for this reason silicone gel implants were approved in the USA by the FDA (Food and Drug Administration).
2. Is cancer screening more difficult with silicone gel implants?
No, breast implants are clear at each imaging examination and do not hinder the early detection of breast cancer.
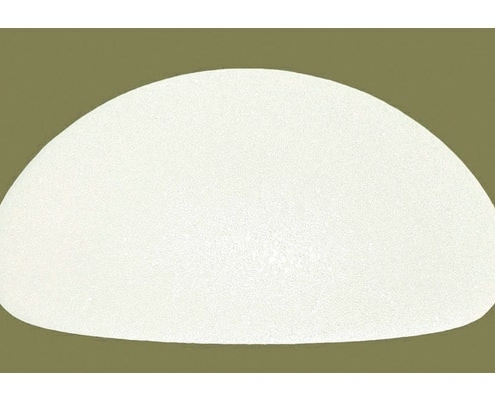
3. Are there other substances in addition to silicone gel, which are used as filling for breast implants?
For a time, in addition to silicone gel and saline solution, soybean oil and starch gels were used. Starch gels proved to be unsuitable due to fluctuations in volume and soybean oil led to toxic degradation of the product. Therefore, there are currently only silicone gel and saline solution implants. Since saline feels distinctly unnatural compared to silicone gel, silicone gel implants are regarded as state of the art.
4. Must silicone gel implants be replaced after several years?
No. ISO 9000, CE certified quality products have no limited shelf life and must therefore not be replaced.
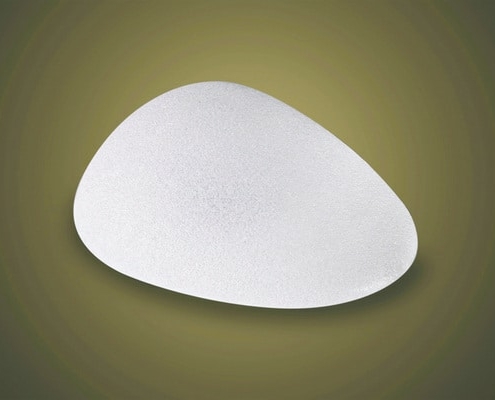
5. There are implants with smooth and textured surface, which are better?
The surface of the implant is important for a number of reasons. Implants with textured surfaces were designed to reduce the chance of capsular contraction. However, textured implants are more likely to be visible through the skin, depending on the implant placement. What is for certain is that textured implants are no worse than smooth.
6. Does silicone gel cause intolerance or allergies?
No, neither. The only possible reaction is capsule contracture, which occurs with a probability of 3-5%, and strictly speaking is not an intolerant reaction to silicone.
7. What is capsular contracture?
The body responds to the “intruder” silicone implant with the formation of a lining. It is usually soft and thin and not noticeable. In about 3-5% of cases, the capsule will tighten, and squeeze the implant. This makes the breast implant feel hard, and distorts the appearance of the breast. In the later stages, the implant feels very firm, and may take on a “ball-like” look. It is important to remember that it is not the implant that has hardened. The shrinking of the capsule compresses the implant, causing it to feel firm/hard. Rarely this may lead to deformation and hardening of the breast and pain.
8. How do you treat capsular contracture?
In surgery, the hardened capsule is cut several times, so it becomes softened and can expand again. Subsequently, the implant is inserted again. This measure is successful in treating approximately 50% of the capsule contractures. If it occurs again, the implant must be permanently removed.
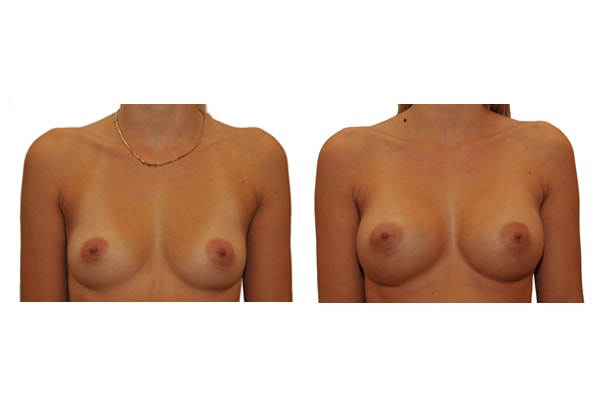
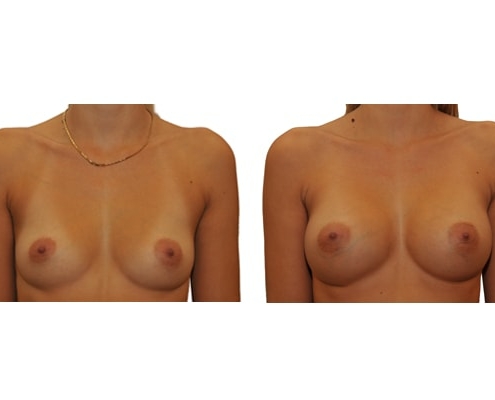
9. At what age and until what age can a breast augmentation be performed?
Breast enlargement should not be carried out prior to 18 years of age. Growth in size and breast growth should be completed. There is no upper limit if you are medically and psychologically sound.
10. Can breasts be enlarged at will?
Limiting factors are the width of the chest and the size of the existing breast. Basically, the smaller the existing breast or the more delicate the chest, the less can be increased. Implants should not protrude over the edge of one part of the chest and skin should not be stretched to the limit.
11. Should implants be placed above or below the chest muscle?
Ideally, implants are placed above the pectoral muscle because they then form a unity with the breast tissue and resonate with natural body movements. They are also hardly discernible. To achieve a natural result, the implant must be surrounded on all sides by soft tissue. If there is not enough volume for a smaller breast, the implant is then placed under the chest muscle to ensure sufficient soft tissue. This placement has the disadvantage that the implant doesn’t move as naturally with the body and is more easily identifiable when touched.
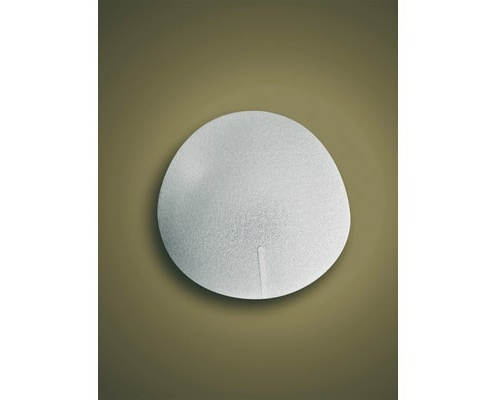
12. There are round and teardrop-shaped implants, which should be used?
That depends partly on the desire of the patient and the other from the planned placement. Round implants accent the neckline, which may well be desired. Teardrop-shaped implants (anatomic implants) are flattened at the top and accent the neckline less. Therefore, they are primarily used when a placement is planned under the chest muscle so that the neckline is not too depressed. In principle the choice of the implant is individual.
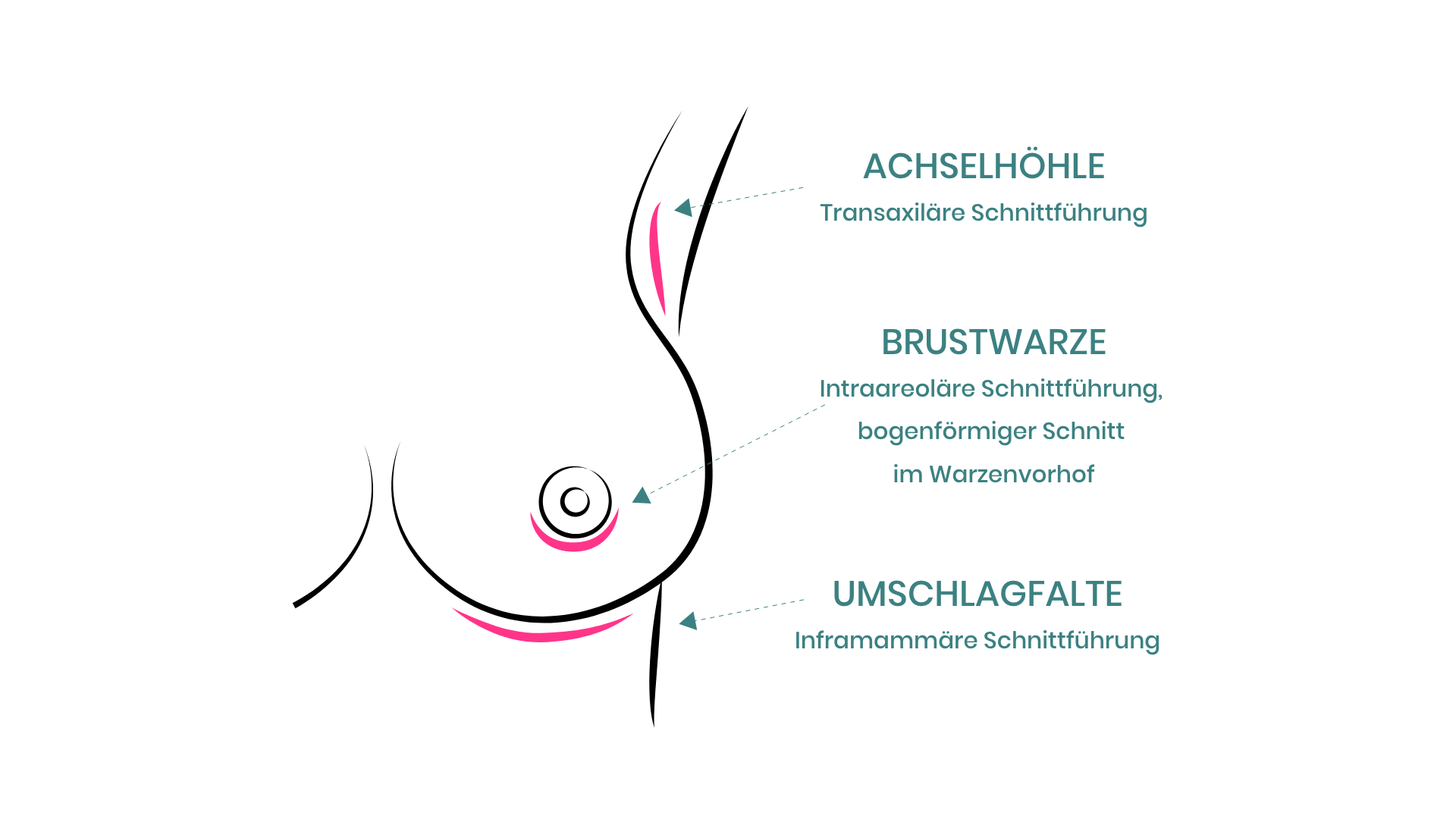
13. There are three possible means of access, which one should you choose?
Regardless of whether one introduces the implant through the armpit, the areola, or the lower side, none of these approaches is better or worse than the other, each has its advantages and disadvantages. According to lifestyle habits, the patient can choose where scar is the least disruptive. When performed correctly, all the scars are almost invisible. For the surgeon, although access is via the lower side is the easiest; he should be skilled in all three access routes and let you choose.
14. Can a breast augmentation be performed by fat grafting?
The autologous fat transplantation, especially when it’s performed with stem cells, is still in its infancy. Currently, the time and operating cost is very high, and the achievable magnification is limited to 250ml. Medically, nothing speaks against it, and if you want a breast augmentation by fat grafting, this can be offered.
15. Can a breast augmentation be carried out under local anesthesia?
I advise my patients on it. In an operation under local anesthesia, the risk of complications based on the witnessing of the operation and the possible stress this can cause, is not proportional to cost savings. In addition, there is only a very low medical risk with general anesthesia, and with good postoperative recovery, you may be able to leave the hospital on the same day.
16. Will I lose the ability to breastfeed with breast augmentation?
Generally not, however, in rare cases, the ability to breastfeed can be slightly affected.
17. Do you lose sensitivity of the nipples with a breast enlargement?
Generally not, however, in rare cases, it can cause a temporary and even rarer permanent worsening of the sensitivity of the nipple and the areola.
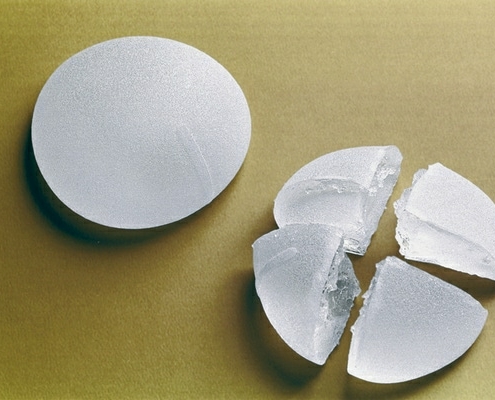
18. What complications can occur?
The most common medical complication is bleeding, followed by infection. When performed correctly, both are very rare. Other complications can include asymmetry, shifting of implants, implants leakage or rupture. All complications can be managed surgically.
19 . How long after the procedure can I resume normal activity?
For a placement of the implants over the muscle, after a few days. For placement under the muscle it may take a little longer.
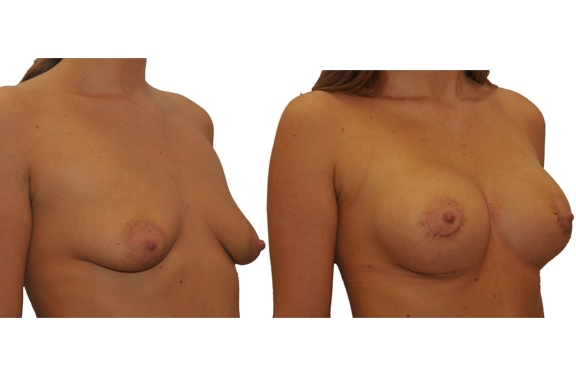
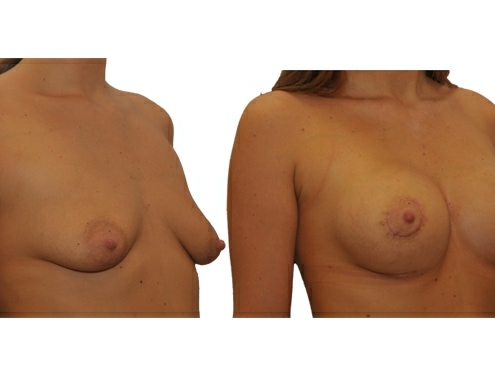
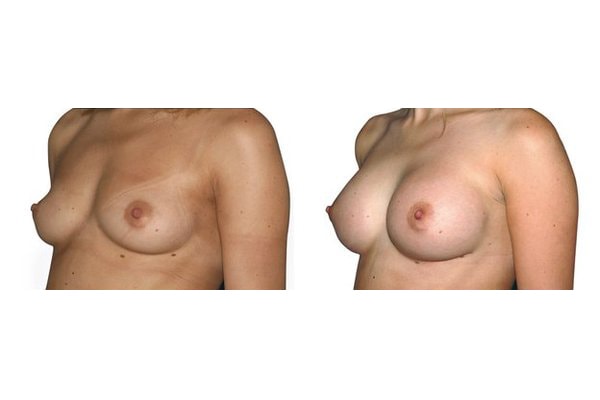
20. What are the long-term results after breast augmentation?
In the vast majority of breast augmentation, the implant heals and the result is natural and long lasting if you keep weight fluctuations and pregnancies limited. Over time, your breasts can change due to aging, weight fluctuations, hormonal factors and gravity. If, after a period of years, you become dissatisfied with the appearance of your breasts, you may choose to undergo a breast lift or implant exchange.